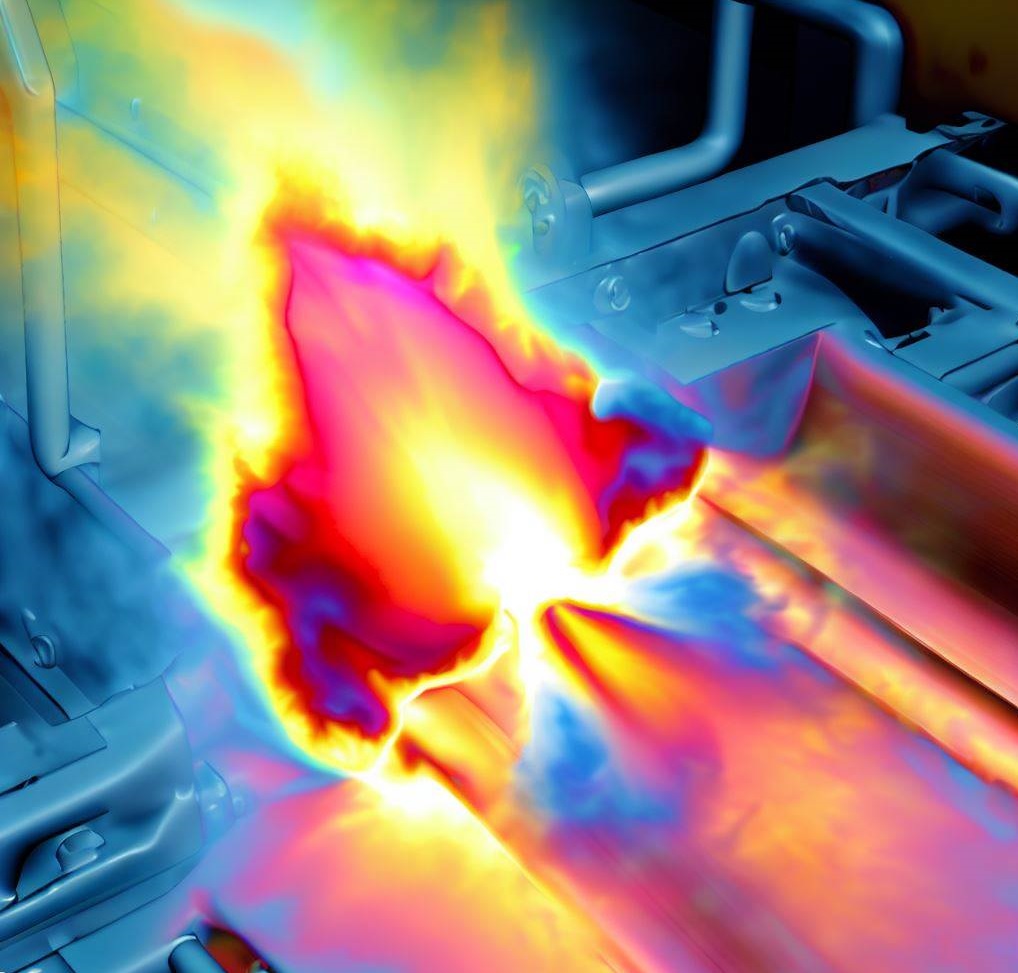
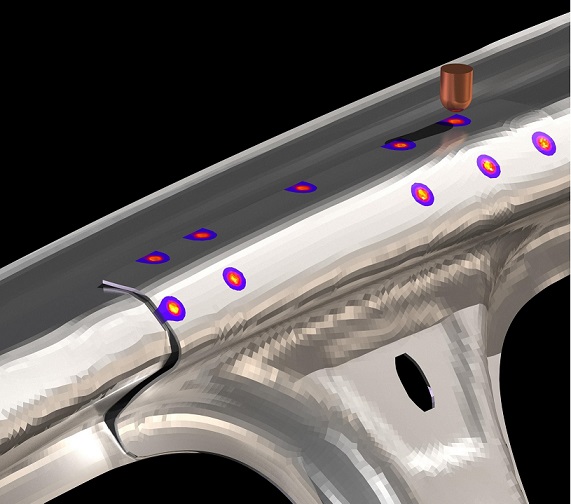
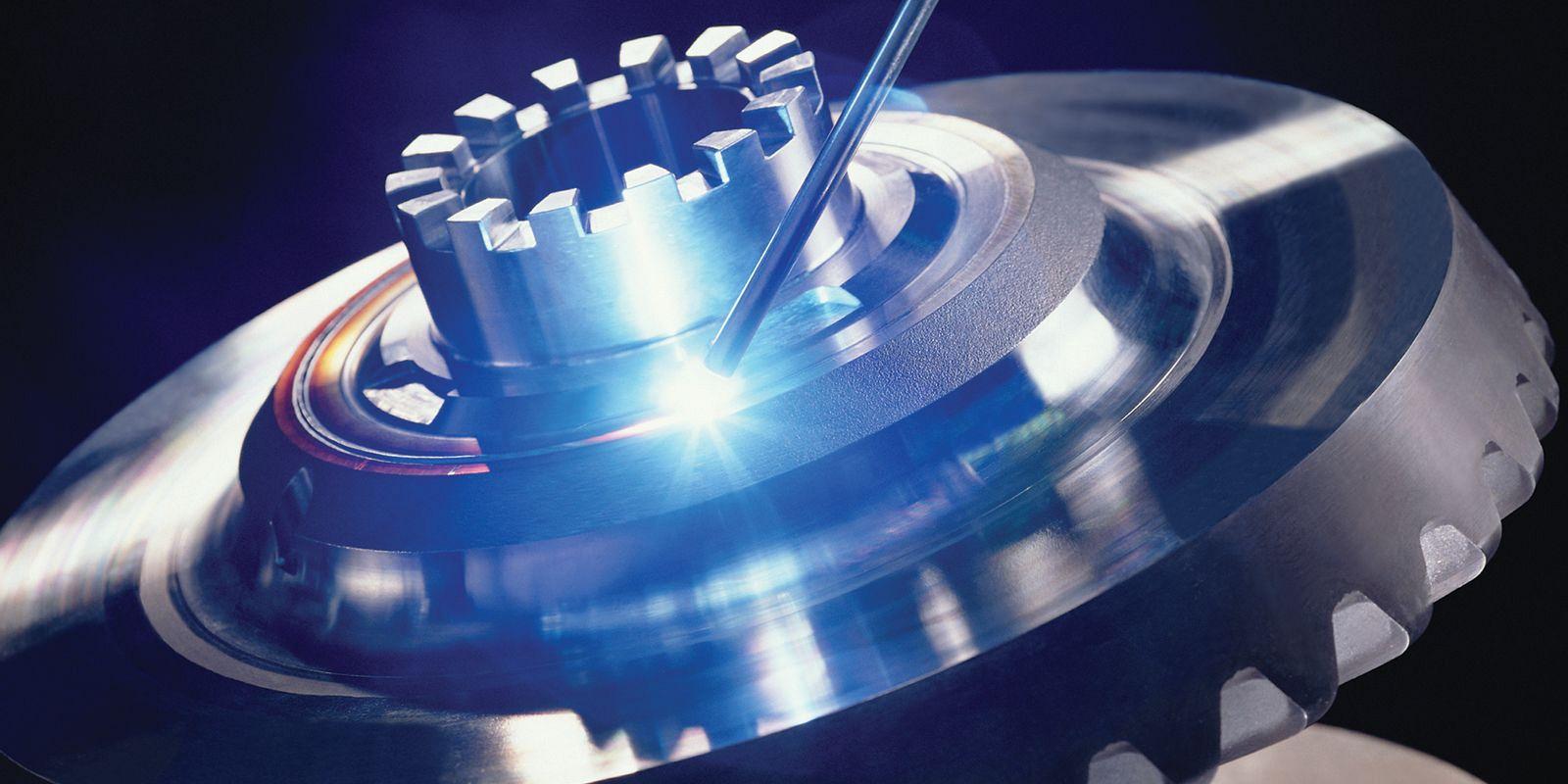
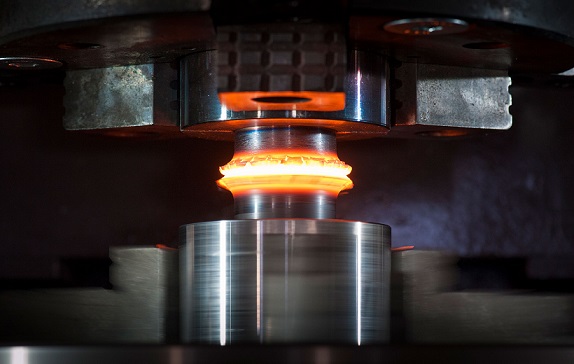
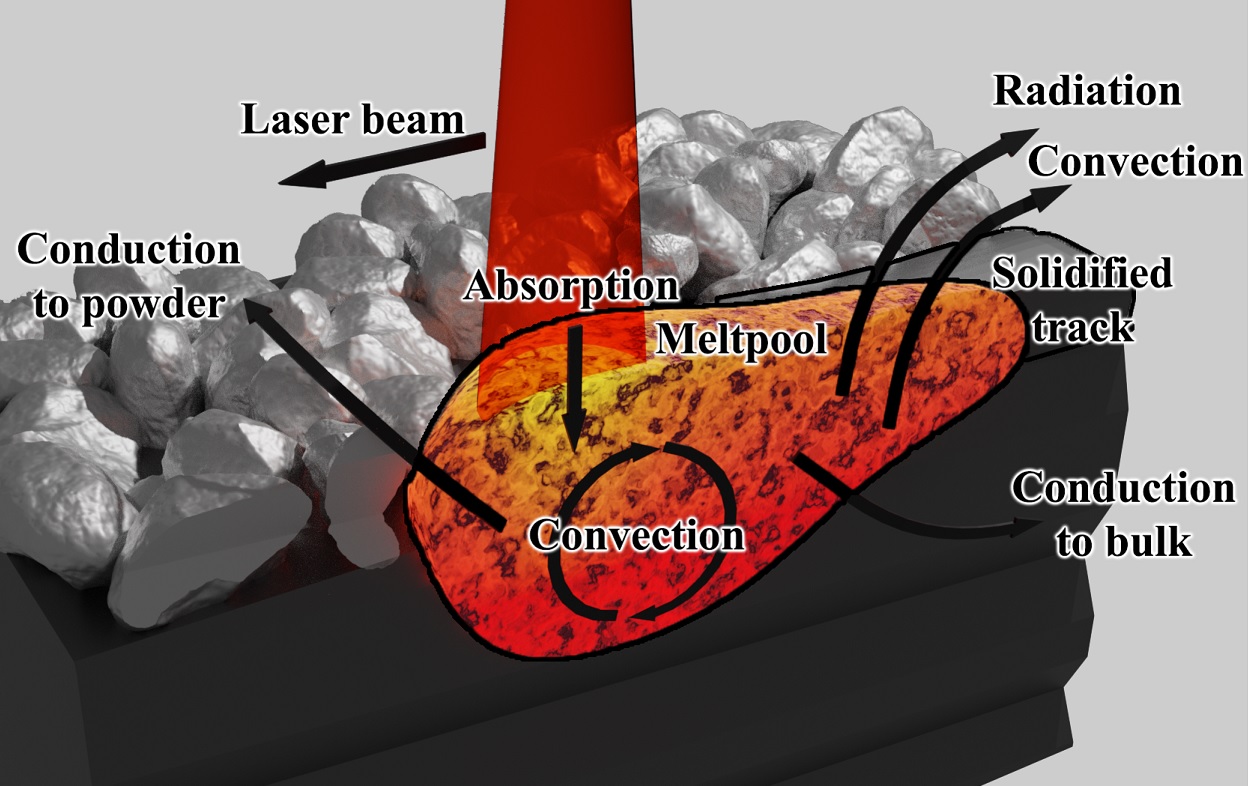
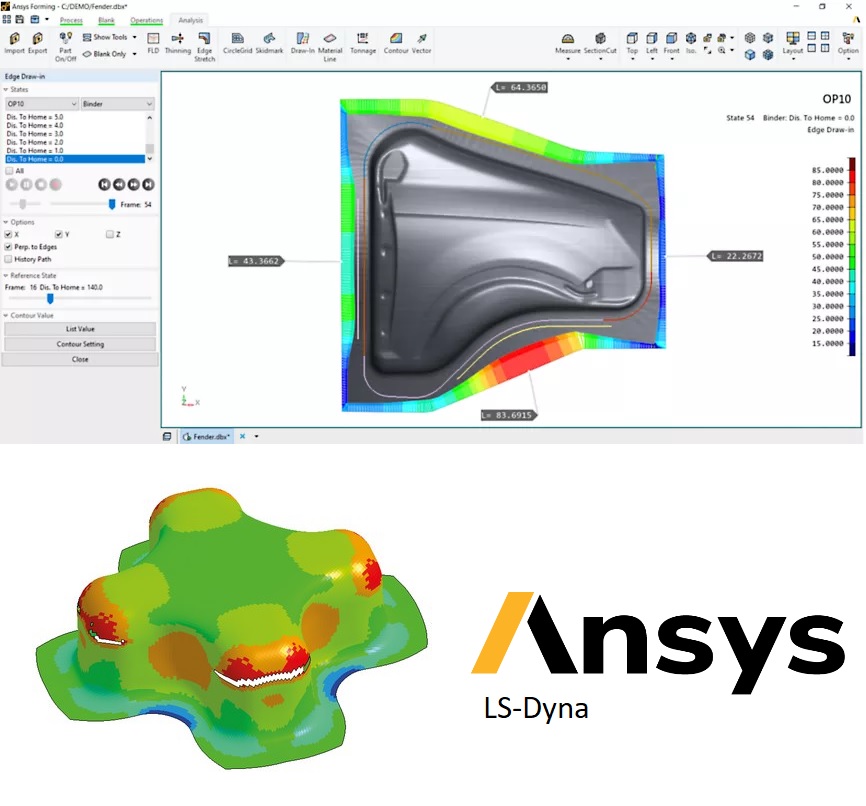
Resistance Spot Welding (RSW) is a pressure welding process used to join two metal sheets together. In RSW, copper electrode welding guns are used to press the sheets together, while an electrical current is passed through them. The heat generated by the electrical current melts the sheets together, creating a small circular welded area between them.
The RSW process is commonly used in the automotive industry for welding body panels and other sheet metal components. It offers several advantages over other welding processes, including high speed, low cost, and the ability to produce consistent, high-quality welds.
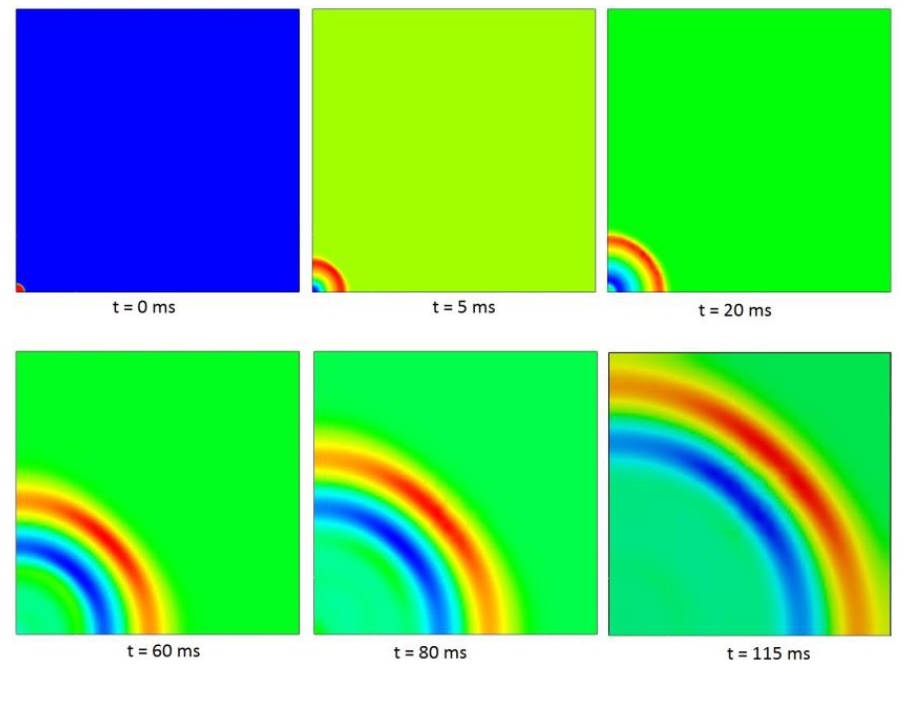
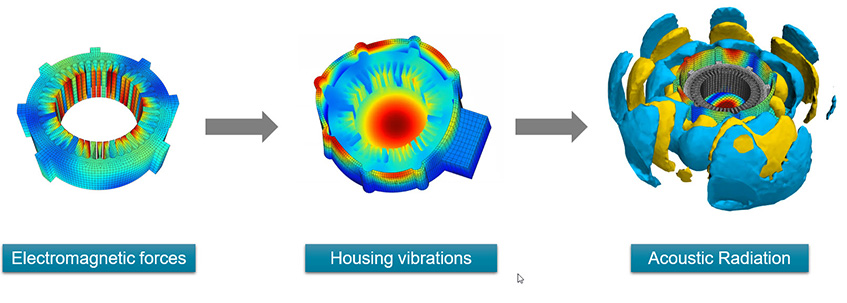
To simulate the RSW process, engineers use computer-aided engineering (CAE) software to model the electrical, thermal, metallurgical, and mechanical behavior of the joint. The software calculates the heat generated by Joule's heating, which is the heating effect caused by the electrical current passing through the metal.
The standard approach in an RSW model involves fully coupled electrical, thermal, metallurgical, and mechanical steps. This means that the software takes into account the electrical resistance, thermal conductivity, melting, and solidification of the metal, as well as the mechanical forces involved in the welding process.
By simulating the RSW process, our engineers can optimize the design of the joint and identify potential issues before the welding takes place. This helps ensure that the joint will meet the required specifications and perform reliably in the intended application.